Elevating Business through Digital Excellence. Your Vision, Our Code.
Our Expertise
Chromex Technologies Expertise| Industry Knowledge| Problem-Solving Abilities| Experience| Innovation| Communication and Collaboration| Communication and Collaboration| Customer Understanding | Quality Assurance | Adaptability
Read moreWeb Design & Development
- Web design - Web development - Custom icons & illustrations - Hosting - Website audit
Read moreDigital Marketing
- Social media marketing - Marketing campaigns - Markting management - SEO
Read moreWe're looking forward to start a new project
Let's take your business to the next level!
Our working process
An Agile software development process is a set of principles and practices that prioritize flexibility, collaboration, and customer feedback to deliver high-quality software efficiently. Agile methodologies were developed as an alternative to traditional, rigid software development approaches, and they encourage iterative and incremental development. Below, I’ll describe Agile software development in detail, including its key principles and processes:
Customer-Centricity
Agile development places the customer at the center of the process. It emphasizes understanding and continuously responding to customer needs and feedback.
Iterative Development
Instead of delivering a complete product at the end of a long development cycle, Agile promotes iterative development. It involves breaking the project into smaller, manageable pieces (iterations or sprints) that are completed within a fixed time frame.
Collaboration
Agile teams encourage collaboration among members, including developers, designers, testers, and product owners. Frequent communication is essential to ensure that everyone is aligned with project goals.
Flexibility
Agile values responding to change over following a plan. It acknowledges that requirements and priorities can change, so it allows for adjustments and adaptations throughout the development process.
Continuous Improvement
Agile teams engage in regular retrospectives to reflect on their processes and identify areas for improvement. Continuous learning and adaptation are fundamental to Agile.
Agile Frameworks and Processes:
Scrum
Kanban
Extreme Programming (XP)
Lean Software Development
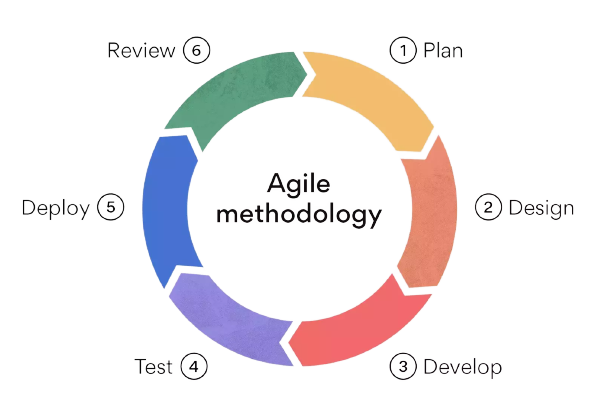
Key Agile Practices:
User Stories: Agile teams use user stories to define features or functionality from the user’s perspective. These stories capture what a user needs to accomplish.
Backlog: The product backlog is a prioritized list of all the features, enhancements, and bug fixes that need to be addressed. It evolves as new information becomes available.
Sprint Planning: At the beginning of each sprint, the team selects a set of items from the backlog to work on during that sprint.
Daily Stand-Up Meetings: Short daily meetings where team members share progress, discuss obstacles, and plan their work for the day.
Sprint Review: At the end of each sprint, the team demonstrates the work completed during the sprint to stakeholders for feedback.
Retrospectives: After each sprint, the team holds a retrospective meeting to reflect on what went well, what didn’t, and how they can improve their processes.
Continuous Integration (CI): Developers regularly integrate their code changes into a shared repository. Automated tests are run to catch integration issues early.
Test-Driven Development (TDD): Developers write tests before writing code to ensure that the code meets the desired functionality.
Pair Programming: Two developers work together at the same workstation, with one writing code while the other reviews and provides immediate feedback.
Frequent Releases: Agile promotes frequent, small releases to get valuable features in the hands of users quickly and gather feedback.
Overall, Agile software development is a flexible and customer-focused approach that empowers teams to deliver value in a collaborative and adaptive manner. The specific Agile framework or practices a team adopts may vary based on the project’s needs and the team’s preferences.




